Consolidate Work
Collect similar work items and work in batches
Rather than addressing each case individually, consolidate multiple cases and execute activities in batches.
Reijers, H., & Liman Mansar, S. (2005). Best practices in business process redesign: an overview and qualitative evaluation of successful redesign heuristics. Omega, 33(4)
Description
Batch processing is an organized method of handling tasks by grouping similar activities together and executing them collectively, as opposed to dealing with each task individually. This systematic approach aims to enhance efficiency and streamline workflows by minimizing transitions between different types of tasks, allowing for a more structured and optimized workflow.
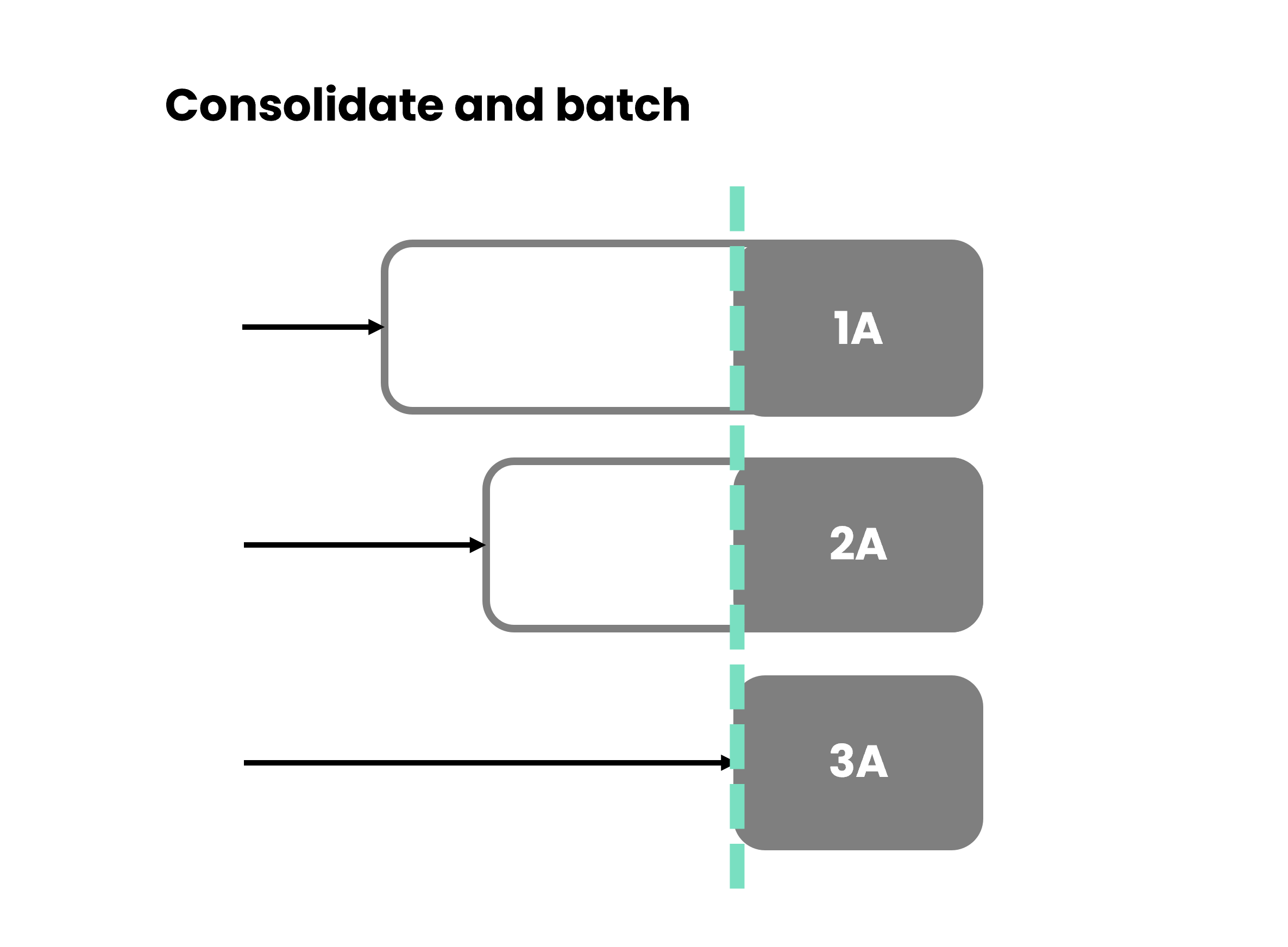
Consider batch processing as a way of categorizing and addressing tasks akin to organizing household chores. Much like cleaning all the rooms at once instead of moving back and forth, batch processing involves identifying tasks that share commonalities, such as similar steps or resource requirements. For instance, tasks like processing invoices or sorting data entries are prime candidates for grouping into batches, allowing for a more efficient and effective handling of these activities.
Application
Batch processing is about figuring out which tasks can be done together because they're kind of alike. For example, if you're processing a bunch of invoices or sorting through data entries, these are tasks that share common steps. So, you group them into batches and handle them more efficiently.
While batch processing offers notable advantages, it is essential to maintain a focus on quality control and flexibility. Ensuring that each batch meets predefined standards is crucial, and the system should be adaptable to changes in task requirements. Regular monitoring of key performance indicators facilitates ongoing optimization. Striking the right balance between batch size and processing time is key to avoiding unnecessary complexity. In essence, batch processing serves as a strategic tool for enhancing efficiency, provided it is implemented with careful consideration of quality, flexibility, and balance.
Performance considerations
The impact of batch processing on performance is analogous to getting more value from your efforts. By concentrating on one batch at a time rather than switching between various tasks, the approach not only accelerates task completion but also optimizes resource utilization. This results in cost savings and improved overall efficiency. Imagine handling paperwork more swiftly and being better equipped to adapt to changing workloads—this exemplifies the positive performance impacts of batch processing.
Share this pattern
Enjoy these
Foundational free Patterns
Eliminate unnecessary activities
Let workers perform as many steps as possible for single cases
Form cross-department teams for end-to-end case handling.
Order knock-outs by least effort and highest termination probability first.
Consider to deepen or broaden the skills of resources
Automate for environmental impact
Implement automation in a sustainable way
Let customers interact with the company wherever they want to
First-contact problem resolution
Establish a one-contact resolution for customer issues
Constraint-based task assignment
Allocate tasks considering business process execution constraints
Share this
Connected to
Buffer external information and subscribe to updates
Combine small activities into composite activities